- Home
- Mandatory Third Party Conformity Assessment
- PSE Mandatory Third-Party Conformity Assessment
The Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law was established for the purpose of regulating the manufacture, sales, etc., of electrical appliances and materials and of fostering voluntary activities by private enterprises to ensure the safety of electrical appliances and materials so as to prevent hazards and trouble caused by the electrical appliances and materials. (Article 1 of the Law)
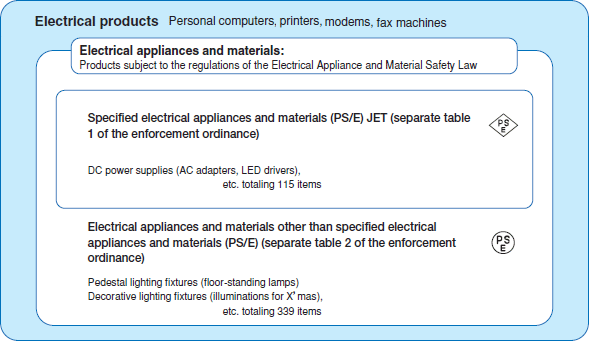
The products subject to the regulations of this law (referred to here as" electrical appliances and materials") refer to the 454 items stipulated by Cabinet Orders, including 115" specified electrical appliances and materials" which, depending on their construction, methods or other conditions of use, pose a serious threat of electric shocks, fire and/or other hazards and trouble. (Article 2 of the Law)
Enterprises engaged in the business of the manufacture or importation of products classified as" electrical appliances and materials" (hereafter, the" notifying suppliers") are obliged to notify the Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry of the commencement of their enterprise (Article 3 of the Law) and conform to the technical standards (Article 8 of the Law) and fulfill other duties, and only those enterprises who have fulfilled these obligations including notification are allowed to display the ![]() and
and ![]() labels as evidence of the fact that they have followed the procedures according to the law. (Article 10 of the Law)
labels as evidence of the fact that they have followed the procedures according to the law. (Article 10 of the Law)
It is absolutely essential for manufacturers or importers of" Electrical Appliances" to follow the appropriate steps and fulfill the imposed obligations, since the sale of any Electrical Appliances and Materials that are not labeled according to the Law (Article 27 of the Law) is prohibited in Japan, and penalties are levied and other punitive actions are taken if the procedures are not carried out.
According to the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law, the following kinds of products are regulated.
- Parts of electrical facilities for general use (meaning electrical facilities for general use as prescribed in Article 38, paragraph 1 of the Electricity Utilities Industry Act (Act No. 170 of 1964)) and machines, appliances, and materials used in connection thereto, as specified by a Cabinet Order
- Portable power generators, specified by a Cabinet Order
- Storage batteries, specified by a Cabinet Order
Specifically, the 454 items stipulated by the Enforcement Ordinances (Cabinet Orders) of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law are specified using the positive list system. (Items related to separate tables 1 and 2 of the Enforcement Ordinance, Article 2 of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law)
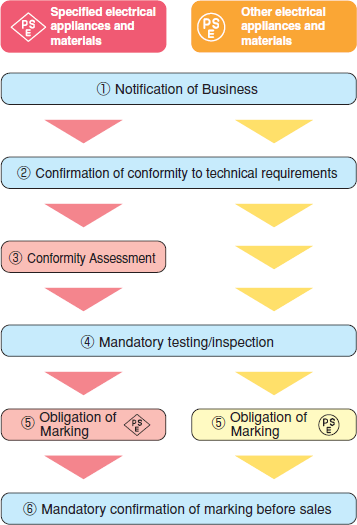
(1)Notification of business (Articles 3 to 6 of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law)
In cases where a manufacturer or importer intends to manufacture or import an electrical appliance that is specified in any of the Enforcement Ordinances of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law, the manufacturer or importer concerned is obliged to provide" notification" in accordance with Article 3 of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law.
(2)Obligation to comply with technical requirements (Paragraph 1, Article 8 of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law)
The notifying supplier is obliged to ensure that the Electrical Appliances that it intends to manufacture or import comply with the technical requirements stipulated by the ministerial ordinances of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry
(3)Conformity assessment (Article 9 of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law)
As for Specified Electrical Appliances, the notifying supplier who intends to manufacture or import them shall: have a Conformity Assessment Body (registered by the Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry) assess their conformity to the technical requirements for each Classified Type prescribed for the notification by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry in order to double-check their conformity which is confirmed in the step (2) shown in the chart on the right, and retain the issued certificates of conformity for the period of their validity stipulated in the Enforcement Ordinance of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law.
(4)Mandatory inspections (Paragraph 2, Article 8 of the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law)
The notifying supplier is obliged to inspect whether the electrical appliances to be manufactured or imported comply with the technical requirements and to prepare and retain the inspection records.
(5)Marking
In order for the notifying supplier to sell electrical appliances, all the above obligations must be followed and the marking shall be put on the electrical appliances in accordance with the method stipulated by the ministerial ordinances of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
(6)Sales
It is prohibited to sell any Electrical Appliances without the marking as the above (5).
Examples of Marking for DC power supplies

Examples of Marking for Pedestal lighting fixtures

Last Update:2011.09.01
